Robots Can Understand Handwriting, Can’t They?

Handwriting may be hard to read even for humans, let alone software robots. Postal change-of-address cards, bank checks, car insurance claims, COVID-19 vaccination records—these and many other kinds of handwritten documents will remain essential to businesses for the foreseeable future. All kinds of organizations need to process handwriting, from public sector agencies like the post office or tax department (such as the United States Internal Revenue Service), to banking and insurance companies, to healthcare organizations.
According to a study done by the Association of Information and Image Management (AIMM), 49% of today’s data capture volume involves paper. There are also many use cases where people enter handwritten information on tablets. So, the ability to ingest and understand handwritten content is critical for automating document workflows and accelerating digital transformations.
Robotic process automation (RPA) solutions have delivered enormous improvements for businesses by automating routine but important tasks to save time, money, and improve overall business operations. However, implementing process automation for handwritten documents is difficult due to the very nature of handwriting.
Whether it is information handwritten on paper or entered on digital tablets, the visual appearance of handwritten text is anything but standardized. It is as varied as the people who put a pen to paper or an electronic screen.
Traditionally, digitizing handwritten documents has involved manual processes. These are time consuming and often inaccurate. They create problems like poor customer experiences and delays in payments. Consequently, this can affect employee performance and morale with repetitive, mundane tasks that take time away from more rewarding activities.
Additionally, most handwriting recognition solutions don’t adequately address the variety of requirements for handwriting processing scenarios, which might be on-premises, in the cloud, or a hybrid.
UiPath Robots can read handwriting
To help our customers address these challenges, UiPath includes a handwriting-recognition engine within UiPath Document Understanding.
UiPath handwriting recognition uses a deep learning model trained on massive dataset containing images of varying degrees of resolution and handwriting styles. Unlike traditional approaches to handwriting processing, the benefit of using deep learning is that our model can make generalizations based on initial handwriting samples, and then the model keeps learning with every data point.
Another benefit of this approach is that the model can learn the context from document elements surrounding the handwritten text and make an educated inference about the handwritten text. For example, if handwriting is entered in fields that appear to be commonly used form blocks—such as a street address or healthcare plan number—the model can interpret the handwriting faster.
How does it work?
The handwriting recognition solution offered as a part of Intelligent Form Extractor relies on the creation of document templates for data extraction.
The Intelligent Form Extractor can find and extract information such as checkmarks, machine text, upper and lower case, cursive handwriting, strikeouts, as well as detect signatures. It is ideally suited for structured forms where users provide handwritten information in predictable fields and locations.
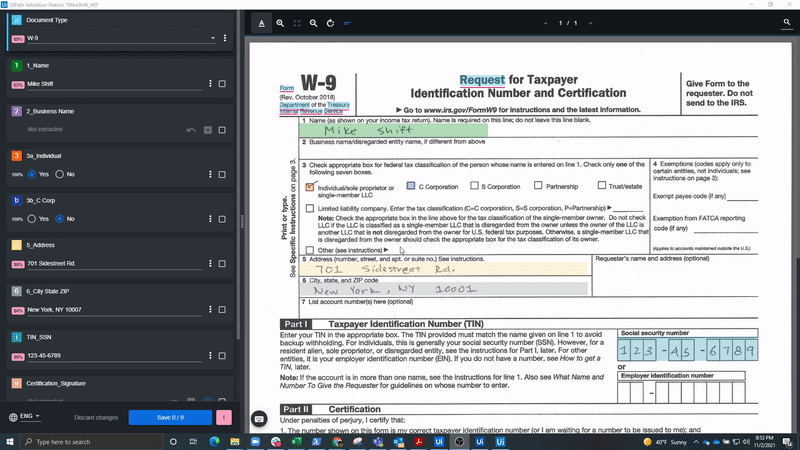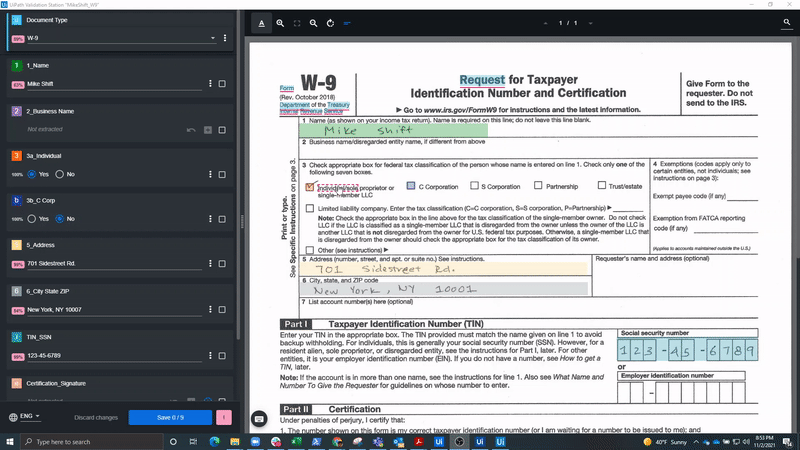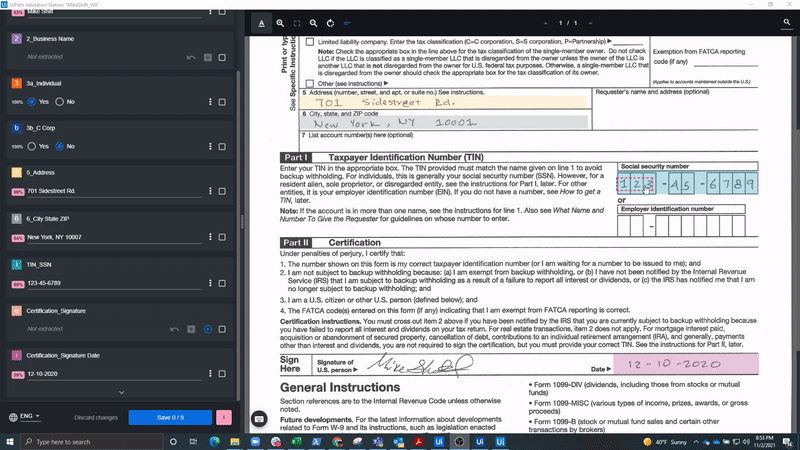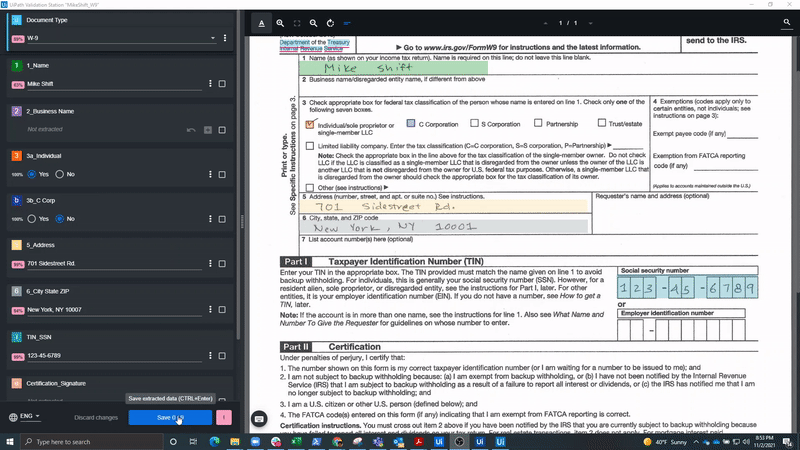
In the following screenshot, we see a W-9, Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification form, which is a commonly used United States (U.S.) IRS form for business owners and independent contractors. As you can see, it includes some handwritten fields and a signature.

When processing such handwritten documents, the user can rely on the high degree of accuracy in the UiPath handwriting engine, which is continuously trained and improved by UiPath. Still, when documents and business needs require additional examination of the handwritten information, they are sent to Validation Station for further review. Here, employees can confirm or correct the extracted fields if the robot isn’t so sure about their accuracy.
Below, you can see how our example W-9 form could be processed and displayed in Validation Station, which is used by business users to manually evaluate the document areas that may be difficult to capture automatically.
Equally important, UiPath supports multi-environment deployment, including cloud, on-premises, and hybrid. This provides enormous flexibility, allowing organizations to implement a powerful handwriting recognition solution according to their specific business scenarios. It is especially important for businesses like financial institutions, healthcare companies, or public sector that need to completely isolate their handwriting recognition processes to adhere to privacy requirements.
One such example among our customers is a major healthcare company in the U.S. The healthcare company wanted to streamline the process of prior authorization for prescribed medications and services. The organization was manually handling millions of such handwritten forms annually, causing delays in authorization and suffering from manual handwriting transcription errors. Further, poor scanning and resolution of such documents exacerbated these issues.
Due to stringent requirements around data privacy and sensitivity and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), the healthcare company was unable to use solutions that would just work in the cloud.
The organization used UiPath Document Understanding to read forms that had a mix of machine and handwritten text. Any extracted value that needed human-in-the-loop verification was sent to the Validation Station. They deployed Document Understanding on-premises to comply with all data privacy regulations.
As a result, the organization was able to successfully read prior authorization request forms and automate the prior authorization process while substantially reducing the error rate.
Automated processing of handwritten information is a challenge—but one that the UiPath handwriting-recognition engine is steadily improving upon.
In a future blog post, I’ll talk about some of the more technical details of using the handwriting-recognition tool. In the meantime, invite your automation team to try out handwriting processing with UiPath Document Understanding.

AI & Product Management, UiPath
Get articles from automation experts in your inbox
SubscribeGet articles from automation experts in your inbox
Sign up today and we'll email you the newest articles every week.
Thank you for subscribing!
Thank you for subscribing! Each week, we'll send the best automation blog posts straight to your inbox.



